Description
MPN: HMB-556
Features:
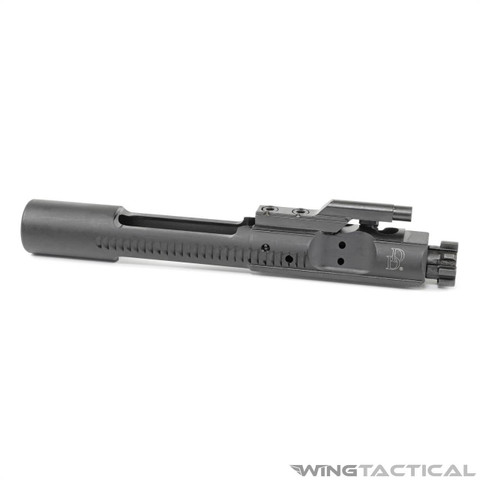
- Drop-in bolt for Mil-Spec carriers
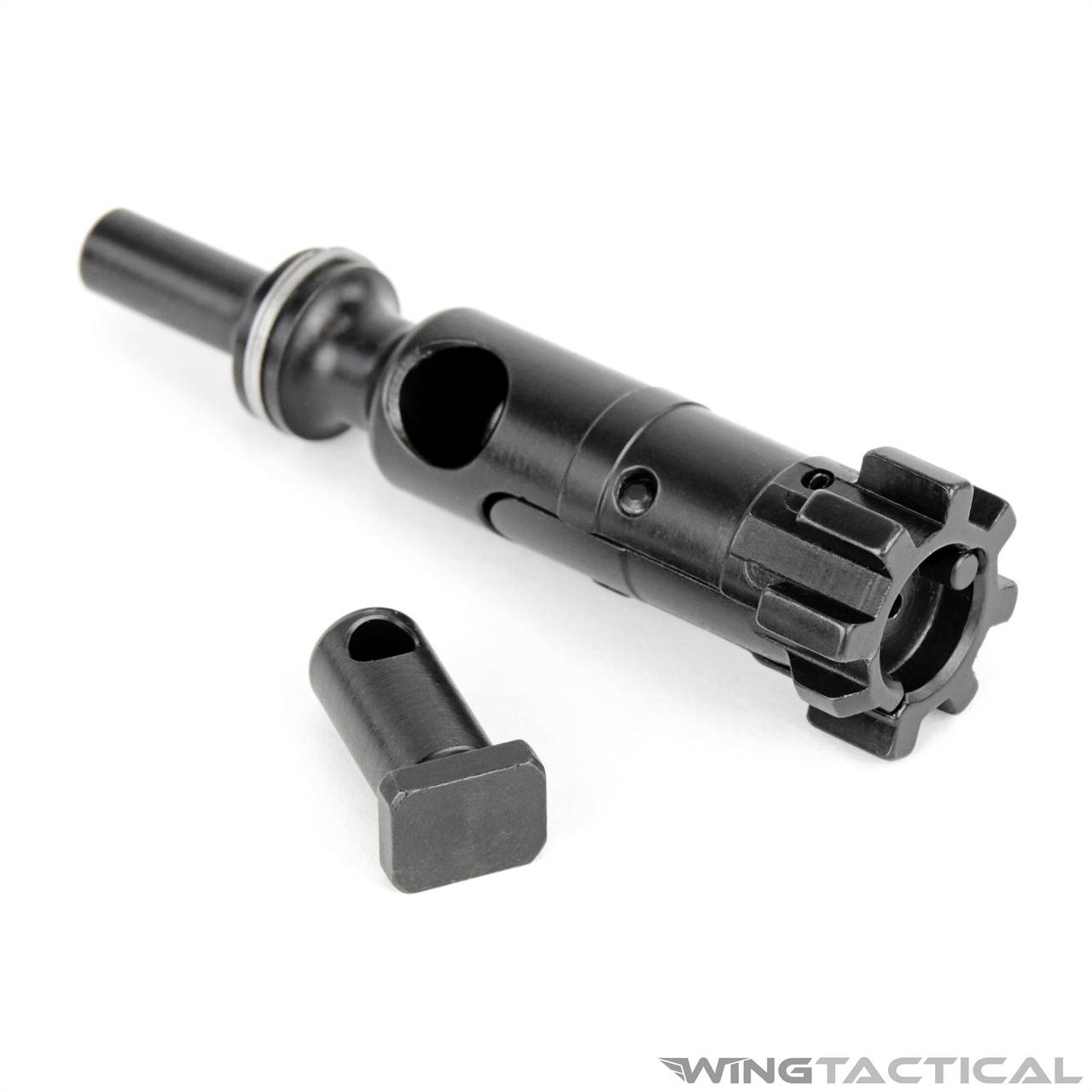
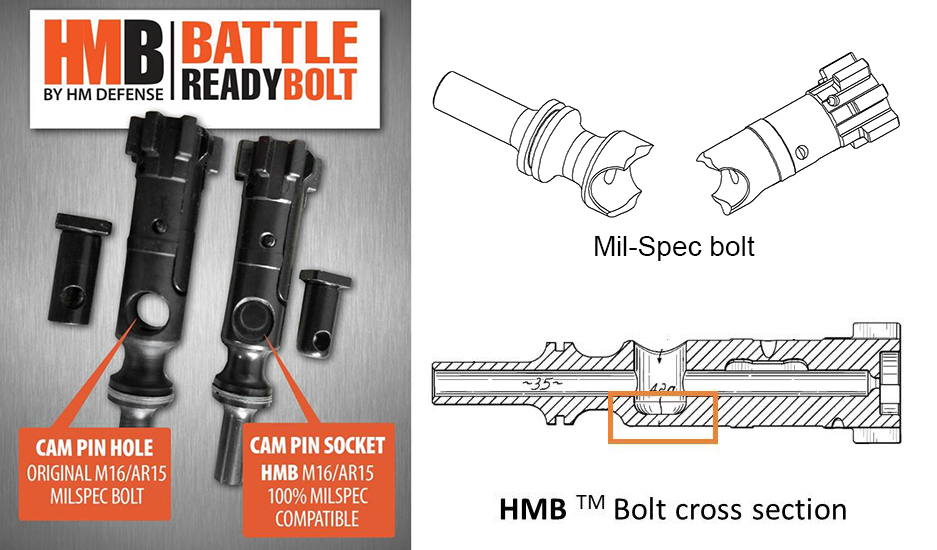
- Eliminates the pass-through cam pin hole
- Significantly increasing the amount of metal at the cam pin location - corrects the natural weak point in existing Mil-Spec bolt
- Substantial improvement in long-term durability over Mil-Spec bolt
- Comes with enhanced tapered cam pin
Specifications:
- Caliber: 5.56 NATO / .223 Rem. / 300BLK
- Material:
- Bolt: 9310 Steel
- Cam Pin: 4340 Hardened Steel
- Finish: Black Nitride
- Weight:
- Bolt: 1.55 oz.
- Cam Pin: 0.25 oz.
Compatibility:
- AR-15
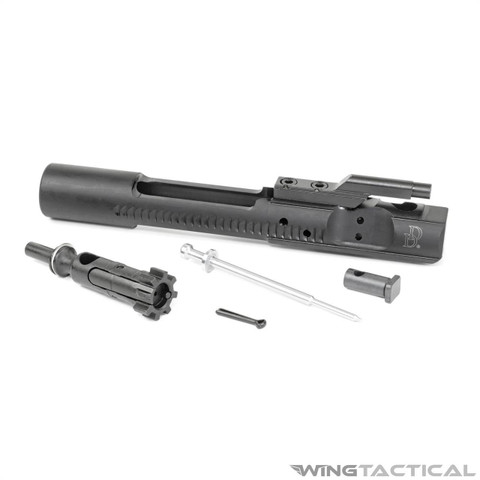
Includes:
- 1x HM Defense HMB Battle Bolt Assembly
- 1x HM Defense HMB Cam Pin
Details:
General Curtis LeMay, got things started for the AR-15 when he ordered a batch of Armalite's new AR-15 rifles in 1961. Decades later, the AR is still in wide-spread use by military, law enforcement and private citizens. Counting all the variants of the AR, an estimated over 13,000,000 of them have been produced. While there have been improvements to the original design, a constant effort continues to bring about more accuracy and reliability to the AR platform. One method for improving the AR’s reliability is the HM Defense Bolt.
Impending Failure
As fine a weapon as it is, the AR’s design has a failure in the making. The bolt of the AR-15/16/M4 and that of the AR-10, have an opening for the cam pin. Possibly for production efficiency, the cam pin hole is drilled straight through the bolt. With heavy usage, or from indifferently manufactured parts, the pressure exerted by the cam pin will eventually crack and ultimately break the bolt.
HM Defense Battle Bolt Solution
The HM Defense bolt eliminates this catastrophic failure with its battle bolt. The cam hole in the HMB bolt is not drilled through. The extra material at the bottom of the bolt gives the HMB bolt increased strength and long-term durability in a critical area. The bolt is compatible with all Mil-Spec AR bolt carrier groups.




















